HHC vs Delta-8 & Delta-9 — A Neutral Comparison for UK Buyers
HHC vs Delta-8 & Delta-9 — here’s a clear, neutral comparison to help UK buyers understand the key differences and what to check when shopping. This article focuses on chemistry basics, product forms, testing (COAs), legal/regulatory signals, and practical buying checks — all without making health or medical claims.
Quick legal reminder
Regulatory status for cannabinoids varies and is actively evolving in the UK. This post is informational only. Always check current rules before buying or promoting cannabinoid products and prefer vendors who publish third-party Certificates of Analysis (COAs) and show clear age verification.
1. Basic chemistry — what’s different? (plain language)
-
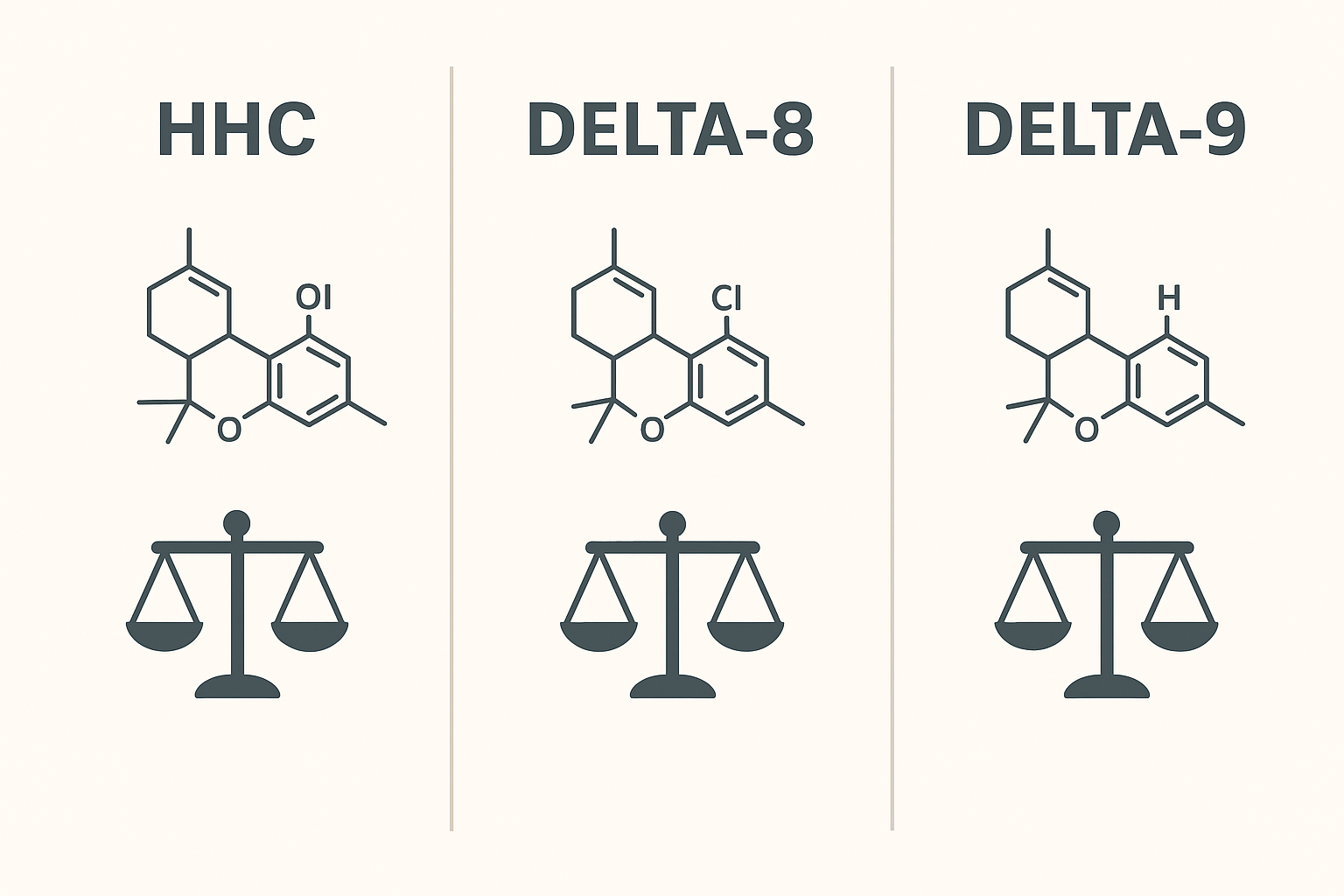
HHC (hexahydrocannabinol): A hydrogenated derivative of cannabinoids; it’s semi-synthetic in many supply chains and may be produced by hydrogenating natural cannabinoids. Its chemical structure differs from THC variants in ways chemists use to discuss potency and stability.
-
Delta-8 THC: A naturally occurring but minor cannabinoid in hemp; often produced at scale through chemical conversion of CBD. It is similar to delta-9 in molecular structure but with a different double-bond location, which some describe as a milder profile.
-
Delta-9 THC: The primary psychoactive cannabinoid found naturally in cannabis. It is commonly regulated and is the reference point for legal frameworks worldwide.
Why this matters for buyers: production method (natural extraction vs conversion/hydrogenation) affects regulatory attention, lab testing priorities, and the potential for residual solvents or byproducts — so always check COAs.
2. Product types you’ll see in the UK market
-
Cartridges & vapes: Common across HHC and delta-8 product lines; check device type (disposable vs rechargeable) given the UK single-use vape ban.
-
Edibles & tinctures: Appear for delta-8 and sometimes HHC; these categories carry different regulatory and lab-testing expectations.
-
Isolates & distillates: Used by manufacturers to formulate cartridges — their purity depends on processing and testing.
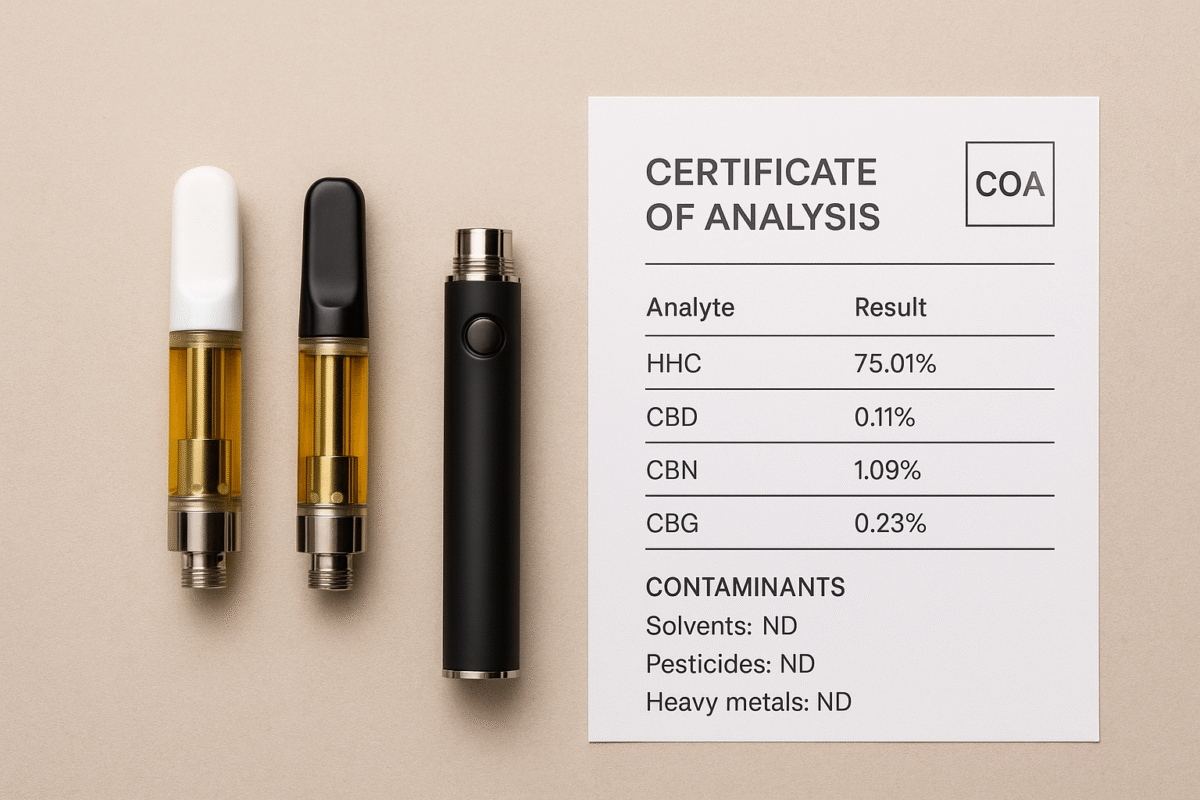
3. Testing priorities — what COAs should show
Independent lab testing is the buyer’s best immediate safeguard regardless of compound.
COA checklist (for any cannabinoid product):
-
Cannabinoid profile: Exact concentrations (mg/g or %) for the cannabinoids present.
-
Contaminant screens: Residual solvents, pesticides, heavy metals, and microbial panels — especially important for chemically converted or semi-synthetic products.
-
Residual byproduct checks: For products made by chemical conversion or hydrogenation, ask whether tests include expected byproducts.
-
Batch ID & date: COA should reference the specific batch you’re buying and be recent.
If a seller cannot produce a batch-specific COA, treat the product as higher risk.
4. Practical legal signals (UK context)
-
Delta-9 THC is the well-known regulated form and is typically subject to strict controls.
-
Delta-8 and HHC have attracted regulatory attention because they are often produced by conversion or semi-synthetic processes; regulators worldwide (and in the UK) are actively assessing how to classify them.
-
Product-type rules (for example, the single-use vape ban effective in 2025) affect how cartridges are sold and which devices are acceptable.
Because of shifting policy, buyers should prioritise COAs, batch IDs, and seller transparency. When in doubt, seek legal/compliance advice before bulk purchasing or promoting these products.
5. Safety & harm-reduction checks for buyers
These are practical, non-medical precautions to reduce risk:
-
Always request a batch-specific COA and verify the date and batch ID.
-
Confirm device type (disposable vs rechargeable) and prefer compliant hardware.
-
Check for residual solvent testing on COAs — conversion and processing can leave traces if not properly purged.
-
Read user reviews for real-world reports on leakage, taste or device issues.
-
Start with small purchases and test tolerance and device compatibility rather than buying large quantities immediately.
6. How to compare side-by-side (quick table you can use when shopping)
-
Compound origin — HHC: often hydrogenation/semi-synthetic; Delta-8: often converted from CBD; Delta-9: naturally present.
-
COA importance — High for all; extra scrutiny for conversion/semi-synthetic routes.
-
Device considerations — Same for all: prefer rechargeable/refillable devices where possible in the UK.
-
Regulatory attention — Delta-9 most commonly controlled; Delta-8 & HHC under active review.
-
Typical consumer notes — Perceived differences in effect are anecdotal; buyer checks should focus on testing and transparency, not subjective claims.
7. Choosing products on the site — practical anchors
When comparing listings, use these anchors to decide:
-
COA present & batch-matched? — If no, don’t buy.
-
Are contaminant panels complete (solvent, pesticides, heavy metals)? — If missing, ask for full testing.
-
Is device type compliant with UK rules? — Avoid single-use disposables unless compliance is confirmed.
-
Does the product list materials and battery compatibility? — Good sign of transparency.
If you want a starting point to compare lab-verified cartridges and specs side-by-side, check a curated hub where COAs and product details are clearly displayed — for example, you can browse our HHC collection or shop HHC cartridges.
8. Common buyer questions (neutral answers)
Q: Is one compound “safer” than another?
A: Safety depends on manufacturing, testing and product handling, not solely on compound name. Prioritise COAs and transparency over marketing claims.
Q: Should I avoid delta-8 or HHC because they’re converted?
A: Conversion methods require additional testing for residual solvents or byproducts — avoid products without full COAs rather than rejecting an entire class by name.
Q: Do COAs guarantee safety?
A: COAs verify what the lab detected for the tested sample and batch. They are a critical transparency tool, but buyers should also check seller practices, batch matching, and device type.
9. Quick pre-purchase checklist
-
Batch-specific COA present and recent
-
Contaminant screens complete (solvents, pesticides, heavy metals, microbes)
-
Device type compliant with UK rules (no disposables unless seller confirms legality)
-
Clear product specs (threading, volume, heating element)
-
Verified reviews and seller contact details
Final thoughts
In the debate HHC vs Delta-8 & Delta-9, the buyer’s focus should be on transparency and testing rather than marketing or hearsay. Production methods and regulatory attention make COAs and batch IDs more important than ever. When comparing products, pick vendors who publish full COAs, clearly label device types, and provide batch information so you can verify what you’re buying.
Related topics about HHC vs Delta-8 & Delta-9
HHC Safety Basics: Storage, Batteries & Best Practices
Understanding HHC & UK Regulations — Plain English Summary
Delta-8/10 HHC Sour Rainbow Gummies 1000mg(Opens in a new browser tab)

 Weed Strains
Weed Strains Hybrid
Hybrid Indica
Indica Vapes
Vapes THC Vapes
THC Vapes Vape Cartridge
Vape Cartridge Disposable Vapes
Disposable Vapes Rechargeable Vapes
Rechargeable Vapes CBD Disposable Vape
CBD Disposable Vape Delta Vapes
Delta Vapes Delta 8 Vape
Delta 8 Vape Delta 9 Vape
Delta 9 Vape smart vape
smart vape Gummies
Gummies CBD Gummies
CBD Gummies THC Gummies
THC Gummies Delta 8 Gummies
Delta 8 Gummies Delta-9 Gummies
Delta-9 Gummies Delta-10 Gummies
Delta-10 Gummies HHC Gummies
HHC Gummies Full Spectrum Gummies
Full Spectrum Gummies Live Resin Gummies
Live Resin Gummies